Assignment topic: A
critical view of Tony Dudley-Evans on English for Specific Purposes
Name: Jinal B. Parmar
Roll no.: 11
M. A. Semester: 3
Paper no.: 12 English
Language Teaching-1
Year: 2014-15
PG Enrolment no:
PG13101025
Submitted to:
Department of English
Smt. S. B. Gardi
Maharaja Krishnakumar
sinhji Bhavnagar University
Introduction:
Tony
Dudley – Evans
Tony
Dudley – Evans was for many years a British linguist and expert in English for
Specific Purposes. He is one of the most influence authors in the development
of the modern notion of genre; he is usually grouped together with John Swales
and Vijay Bhatia as the driving force behind recent development in English for
Specific Purposes.
Introduction:
English
for Specific Purposes
English
for Specific Purposes or English for Special Purposes has for about 30 years
been a separate branch of English Language Teaching. ESP has developed its own
approaches, materials and methodology and its generally seen as a very active,
even ‘feisty’ movement that has had considerable influence over the more
general activities of TESOL – (Teachers of English to Speakers of Other
Languages) and applied linguistics,
Definition:
English
for Specific Purposes
English for Specific Purposes is
a subdivision of a wider field, language for Specific Purposes, which is
defined as:
“……the area of inquiry and practice in the development of
language programs for people who need a language to meet a predictable range of
communicative needs”
English for Specific Purposes
arose as a term in the 1960s as it became increasingly aware that general English
courses frequently did not meet learner or employers needs. ESP involves
teaching and learning the specific skills and language needed by particular
learners for particular purposes.
In ESP in that P is always a
professional purposes a set of skill that learners currently need in their work
or will need in their professional careers. This ESP can be taken to include
business skills, such as English for Job finding or Presentation. Many of the
learners prefer this specific English to learn.
Now-a-days many of the
Universities across the globe are offering a number of ESP course. For example
Dudley-Evans
says that the key defining feature of ESP is that it’s teaching and materials
are founded on the results of Needs Analysis.
“Needs Analysis is fundamental to an EAP- (English for Academic
Purposes) approach to course design and teaching”
In ESP
course there is concern about student’s skill to learn English, which genres do
they used or need to master. ESP is totally opposed from the ‘General English’.
In ESP one can be more precise about learner’s need, their needs are defined by
a learning or occupational situation in which English plays a key role. In
learning of English specific needs can be identified by examining that
situation and the texts in detail, in contrast means in the learning of general
English for students not immediately using English.
Robinson gives her first overview of ESP, and she suggested
that limited duration and adult learners are defining features of ESP courses.
In this she says that limited duration to learn ESP it means an intensive
course of a fixed length and also says that these type of ESP courses learners
are always Adult who grown up their learning easily. Robinson in her second
survey, she accepts that, many of the ESP courses are of limited duration, a
significant number are not there for example,
“A three or four year programs as part of a university degree”
The majority of ESP learners are
adults ESP can be taught at school in English medium schools where English is
not the children’s first language. ESP is generally taught to intermediate or
advanced students of English but can also be taught beginners.
Dudley-Evans
adds his idea also to in ESP it may be designed for specific discipline or
professions. He is also says about teaching methodology of ESP courses. He says
that SEP teachers must aware and knowledgeable about specific English or
subject knowledge, which leads to classroom interaction and teaching
methodology that can be totally different from General English. In ESP courses,
sometimes learner faces difficult situation for example, pre – work or pre –
study courses where learners have not started their academic or professional
activity and therefore have less subject knowledge for them teaching
methodology will be similar to that of General English.
In the
learning of ESP and General English there are vast differences in grammar level
and also in teaching level. There are major differences between ESP English and
General English.
There
are the major differences between ESP English and General English but there are
also some common thing in both of the these ESP English and General English.
Common things in both ESP English and
General English:
Testing
for English for Specific Purposes:
There
are three views of ESP testing
•
In the field of ESP testing has been as a separate and distinctive part of
a more general movement of English language testing, focusing on measuring
specific uses of English language among identified groups of people such as , doctors, nurses, lawyers
, civil engineers, tour guides, air traffic controllers, and others
•
ESP testing has been viewed in the broader context of the teaching and
learning process. According to Dudley-Evans and St. John assessment does not
stand alone but occupies a prominent place in the ESP process, giving an ESP
teacher a wealth of information on the effectiveness and quality of learning
and teaching. As assessment interacts with needs analysis and is dependent on
syllabus design.
•
In ESP tests enhance the learning process and act as a learning device. In
the words of Dudley-Evans and St. John an ESP test is “an aid to learning”.
Moreover assessment evaluates the benefits of learning; tests can give learners
a sense of accomplishment and a feeling that the teacher’s evaluation matches
what skills and knowledge have been covered. Dudley-Evans and St. John add that
assessment “encompasses benefits such as reinforcement, confidence building,
involvement and building on strengths”.
Dudley-
Evans defining the features of ESP looking closely at ‘Specific Purposes’, ESP materials
will always draw on the topics and activities of that specific purpose, in many
cases exploiting the methodology of the subjects area or the profession. For
example, student of engineering they study an English course for engineer will
use engineering situations to present relevant language and discourse,
problem-solving activities will probably also be used, since they drew on
skills and abilities possessed by the students.
Similarly,
a business English course will use studies as these are widely used in business
training. ESP is concerned with teaching language, discourse and relevant
communication skills:it exploits topics and the underlying methodology of the
target discipline or profession to present language, discourse and skills.
Dudley-Evans sees the absolute
characteristics of ESP:
The variable characteristics are:
·
ESP may be related to or designed for specific
discipline.
·
ESP may use, in specific teaching situations, a different
methodology from that of General English.
·
ESP is likely to be designed for adult learners either at
a tertiary level institution or in professional work situation. It could, however be used
for learners at secondary school level.
·
ESP is generally designed for intermediate or advanced students most ESP
courses assume basic knowledge of the language system, but it can be used with
beginners.
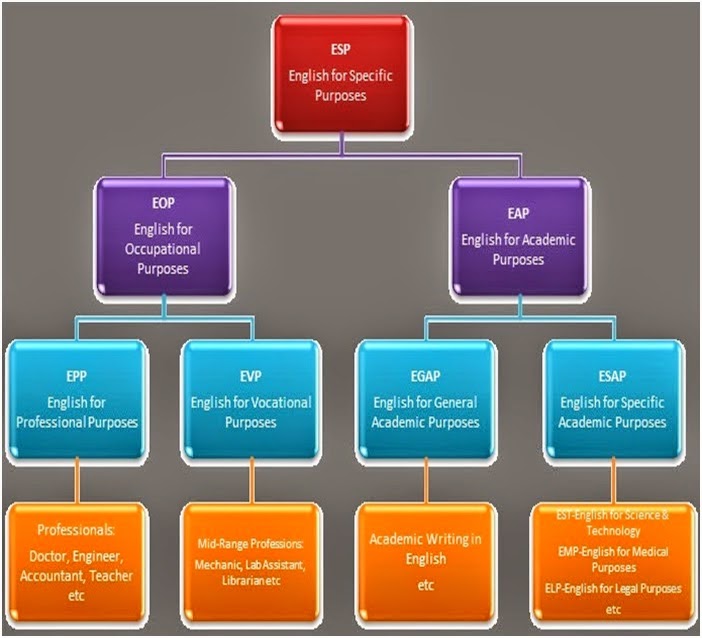
Subject specific ESP:
ESP is
often divided up into various categories with mysterious acronyms. It is
usually classified into two categories EAP and ESP.
English
for Academic Purpose largely for itself it relates to the English needed in an
educational context, usually at university or similar institution, and possibly
also at school level.
English
for Occupational Purposes is very complicated it relates to the professional
purposes for example, those of working doctors, engineers or business people.
The biggest branch of English for occupational purposes is business English. In
business people use to high language to communication. In this EOP the teaching
general business related vocabulary to the teaching of specific skills
important in business, e.g. negotiation and meeting skills.
In ESP
another key distinction is between more general ESP and more specific ESP
Dudley-Evans and St. John drawing on an idea from George Blue – make a
distinction between English for General Academic Purposes (EGAP). Designed for
pro-study groups, or groups that are heterogeneous with regard to discipline
and English for Specific Academic Purposes (ESAP) designed to meet specific
needs of a group from the same discipline.
A
similar distinction can be made between the teaching of general business
related language and skills (English for General Business Purposes – EGBP) and
the teaching of specific business language for skill such as negotiation, or
the writing of letters or faxes (English for Specific Business Purposes – ESBP)
In ESP
it is often convenient to refer to types of ESAP or ESBP by profession, so one
commonly hears terms such as quick medical English, English for engineers or
English for administration. These terms may be useful as a quick
classification, but may lead to confusion.
Medical
English may include EAP for students following a degree course in medicine
where English is the medium of instruction, or a reading skill course where the
subjects taught in a language other than English but also a type of EOP for
practicing doctors using English to talk to patients or to write up research in
English.
In
same way English for engineers may be for students of engineering, or for
practicing engineers needing, say, to write reports in English. In the USA,
ESAP is often called “content- based instruction (CBI)”, which is seen as
separate from ESP.
In
ELT these all types of specific courses is totally separate from General
English. In ESP two other commonly used abbreviations are EST (English for
Science and Technology) which was widely used when most EAP teaching was for
students of engineering and science. It is thus a branch of EAP. In the USA,
EVP (English for Vocational Purposes) is frequently used for teaching English
for specific trades or vocations. This branch of EOP is often subdivided into
Vocational English (concerning language and skills needed in a job) and
pre-vocational English (concerning skills needed for applying for jobs and
being interviewed).
Needs Analysis
“Needs analysis also known as needs assessment and it has vital
role in the process of designing and carrying out any language courses, whether
it be English for Specific Purposes or General English course.”
The
initial needs analysis provides information about target situation what
learners will have to do in English and the skills and language needed. This is
generally called “Target Situation Analysis.”
“The term Target Situation Analysis was infect, first used by
Chambers in his 1980 article in which he tried to clarify the confusion of
terminology. For Chambers TSA is “communication in the target situation”.
In ESP
there is always be the first step is needs analysis it is usually the next
stage that involves the most detailed analysis, and there has been increasing
emphasis on investigating these increasing emphasis on investigating these
additional factors. Information about the learners – in particular their level
in English, weaknesses in language and skills needed and also their own
perceptions of what they need are increasingly investigated. In TSA we find
that learner’s objective need to understand the lecture.
Learning
Situation Analysis is totally different and opposed to the TSA. In this LSA
there is need to study the learner’s confidence or lack of confidence in their
listening abilities, and their perception that they need more vocabulary to
understand lectures is subjective. This investigation of subjectivity is called
“Learning Situation Analysis”.
The
investigation of learner’s weaknesses or lucks is called “Present Situation
Analysis”. As Dudley-Evans and St. John state “A present Situation Analysis
estimates strengths and weaknesses in language, skill, learning
experiences”. If the destination point
to which the students need to get is to be established, first the starting
point has to be defined, and this is provided by means of PSA.
Dudley-Evans and St. John suggest that means analysis
provides us “information about environment in which the course will be run” and
thus attempts to adapt to ESP course to the cultural environment in which it
will be run one of the main issues means analysis is concerned with is an
“acknowledgement that what in works well in one situation may not work in
another”. For example, if learners are used to rote-learning, it may be that a
problem-solving approach to learning ESP will be alien to their learning styles
and contrary to their expectations.
The Need for Text Analysis:
In
this entire article Dudley-Evans’s ESP much priority is given to needs analysis
and the various approaches. Dudley-Evans believes that the key stage in ESP
course design and, materials development is the action needed following this
needs analysis stage. This next stage is when the ESP teacher considered the
texts that the learner has to produce and understand, tries to identify the
text’s key features and devises teaching materials that will enable learners to
use the texts effectively.
In
early work in ESP genre analysis placed the focus on ‘moves’, i.e. how the
writer structures a text or part of a text through a series of stratagems.
Masuku argues that moves and genres are elements of discourse and that the
difference between them is that moves combine to form genres. At a rank below
the move ‘we enter the domain of grammar’.
A move
may be defined as “a meaningful unit represented in linguistic forms and
related to the communicative purpose of the social activity in which members of
the discourse community are engaged.”
ESP school is considering higher level issues, research
using corpora and concordancing techniques has linked genre analysis with
phraseological studies. Gledhill introduces the medical article about cancer
research use a limited and predictable phraseology. This phraseology can be established
by examining the collocation of high-frequency grammatical items. This research
has great potential, esp. the potential of relating the more general findings
of genre analysis to specific language use, and thus to materials production.
The
current growth area in ESP concern with the discourse community’s work is also
characteristic of the teaching of business English. Needs analysis in business
English must establish exactly how the discourse community uses language and
text, and the effect of culture on the way that discourse is structured.
Dudley-Evans
argued that ESP is a materials-led field. Most materials, however, are prepared
by individual teacher for particular situation, and there is not a huge amount
of published ESP material. In English for occupational purposes there are
especially business English materials.
ESP Syllabus Design:
In
ESP syllabus designing abilities like develops required in order to
successfully communicate in occupational setting is the ability to use the
particular jargon that is characteristic of the specific occupational context.
The second is the ability to use a more generalized set of academic skills and
the third is the ability to use the language of everyday informal talk to
communicate effectively, regardless of occupational context.
The
task for the ESP developer is to ensure that all three abilities are integrated
into the syllabus.
ESP syllabus design should cover the
three factors:
Factors affecting ESP course design:
Conclusion
In conclusion
I would like to threw some light on Dudley-Evans’s views regarding ESP. he
argued for the importance of Genre analysis as applied research that leads the
course designer from the initial needs analysis to materials production and
lesson planning.
Dudley-Evans
suggested on the basis of research into the discourse and researchers can have
an increased role as “Genre Doctors” advising discipline and professions on the
effectiveness of their communication.
For
the teachers and learners ESP is more challenging course because ESP has its
own movement, its own journal and its own procedure.











No comments:
Post a Comment